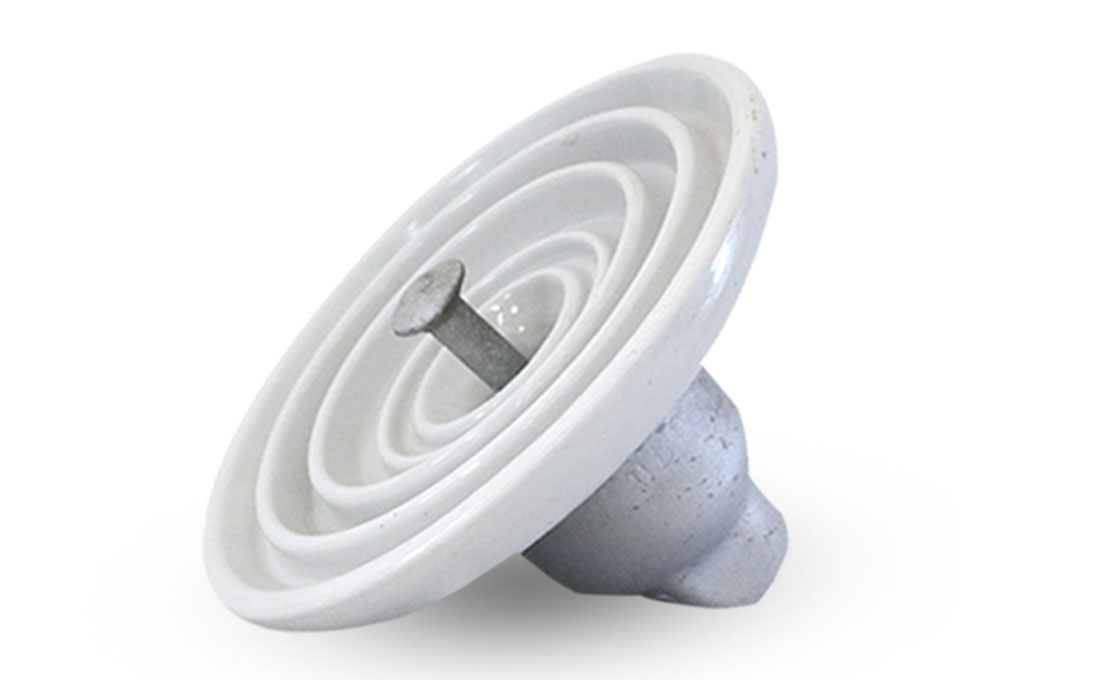
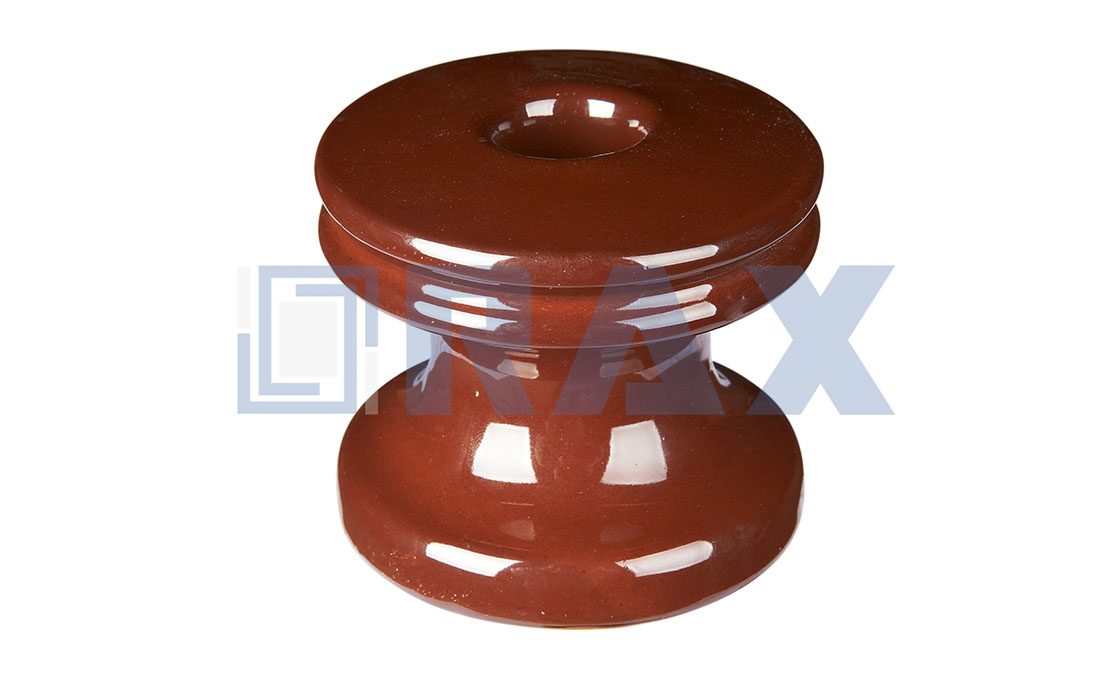
Suspension Insulator
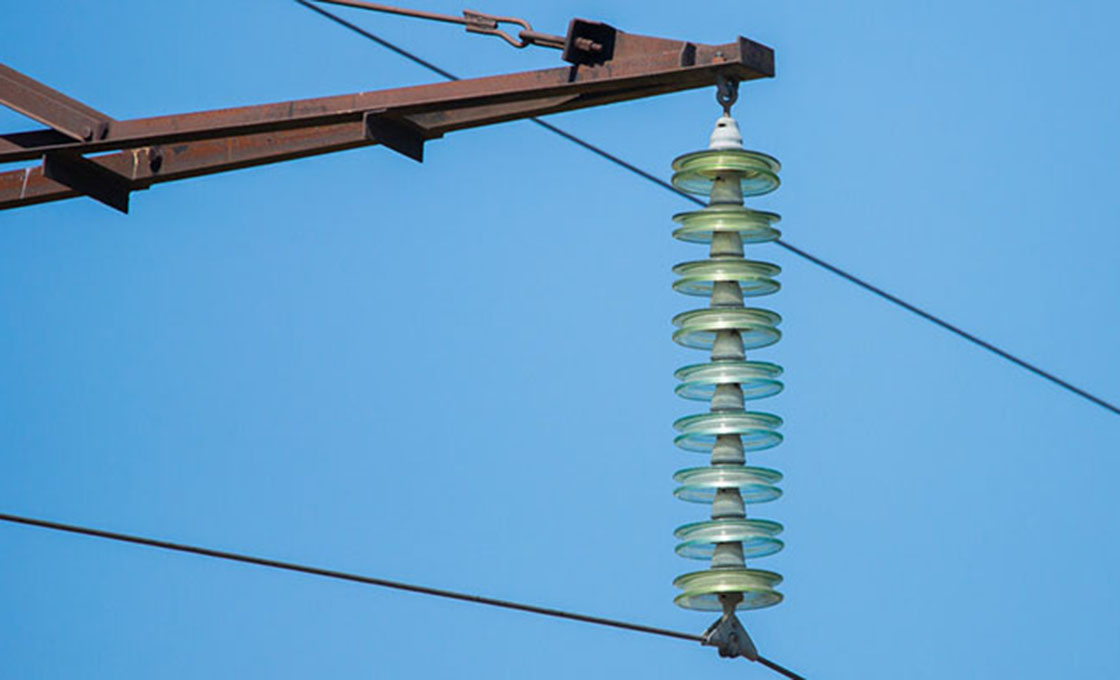
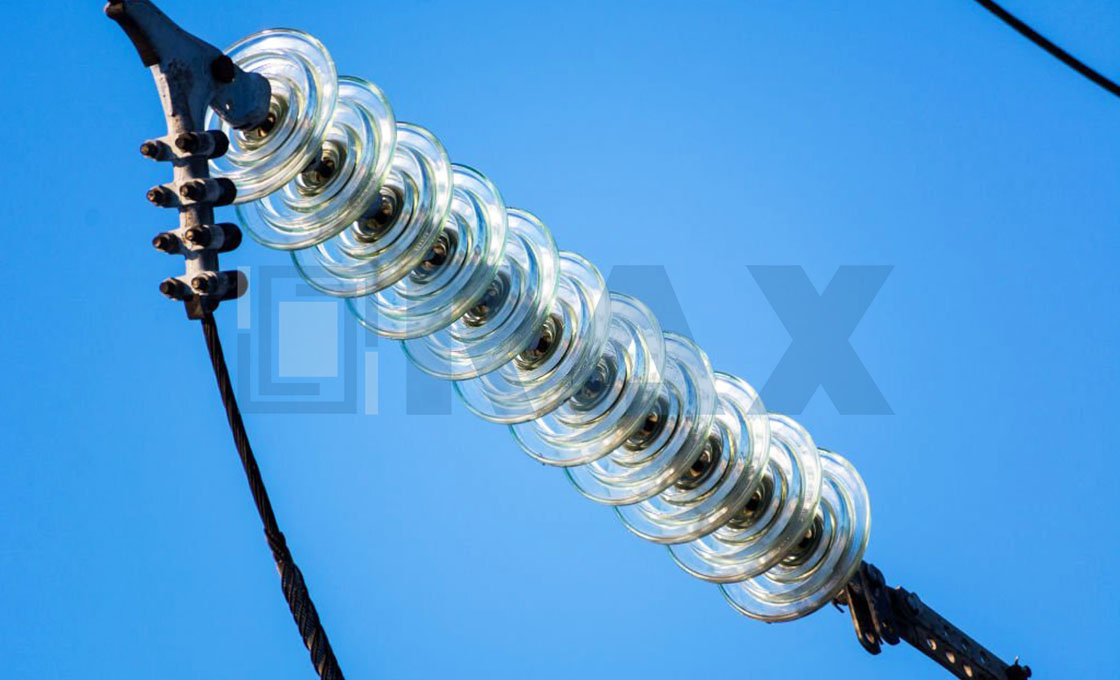
Just the same as the string insulator, a suspension insulator is a flexible insulator string that consists of some porcelain or glass disc insulators connected with each other by metal connections. It is widely used in medium and high voltages of transmission lines.
There are two types of suspension insulators: cap and pin insulator and interlink insulator (also known as Hewlett type insulator), they are two designs and connected with different metal connections.
For the pole lines where the conductor is suspended from the insulator’s bottom section, cross-arms are used for securing the insulator in place. The cross-arm ensures that the insulator remains stable when connected to the pole or tower.
The voltage capacity of the insulator is dictated by the disc plates. The more the plates the higher the voltage capacity.
Types of end fittings can be mounted to the suspension insulator, such as Y-clevis, tongue, clevis, socket, ball, and eye.
There are some differences between suspension insulators and string insulators. The suspension insulator is used in the vertical position withstanding its own gravity, while the string insulator is mounted horizontal bearing a certain amount of tension of conductor.
To know more about the suspension insulator, please contact us now.
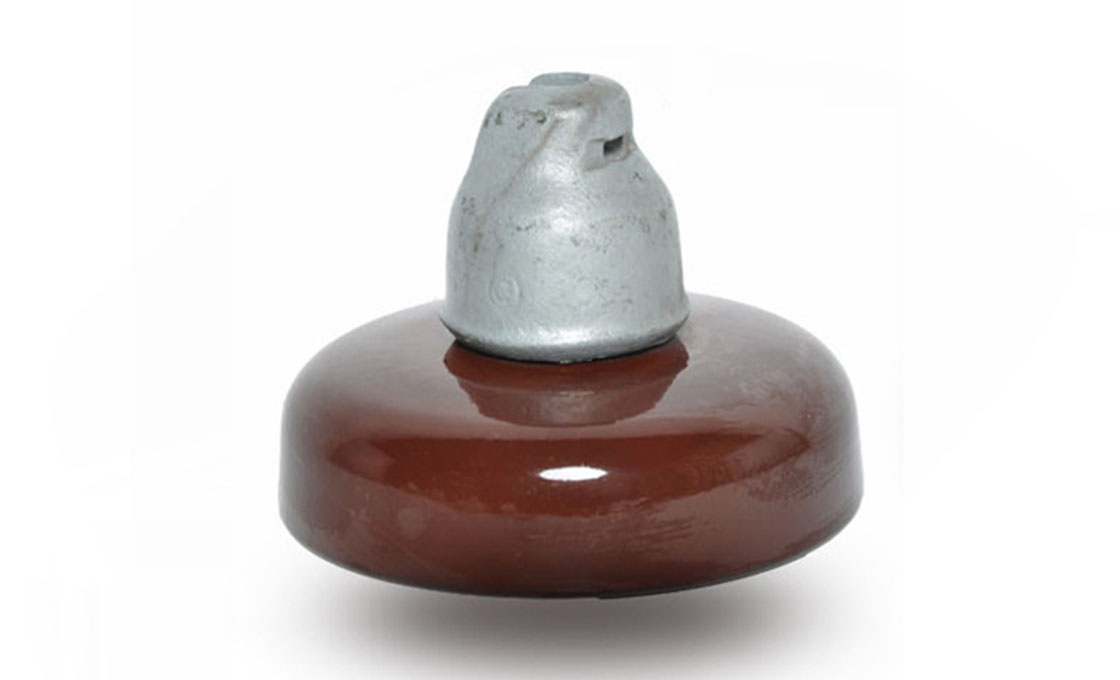
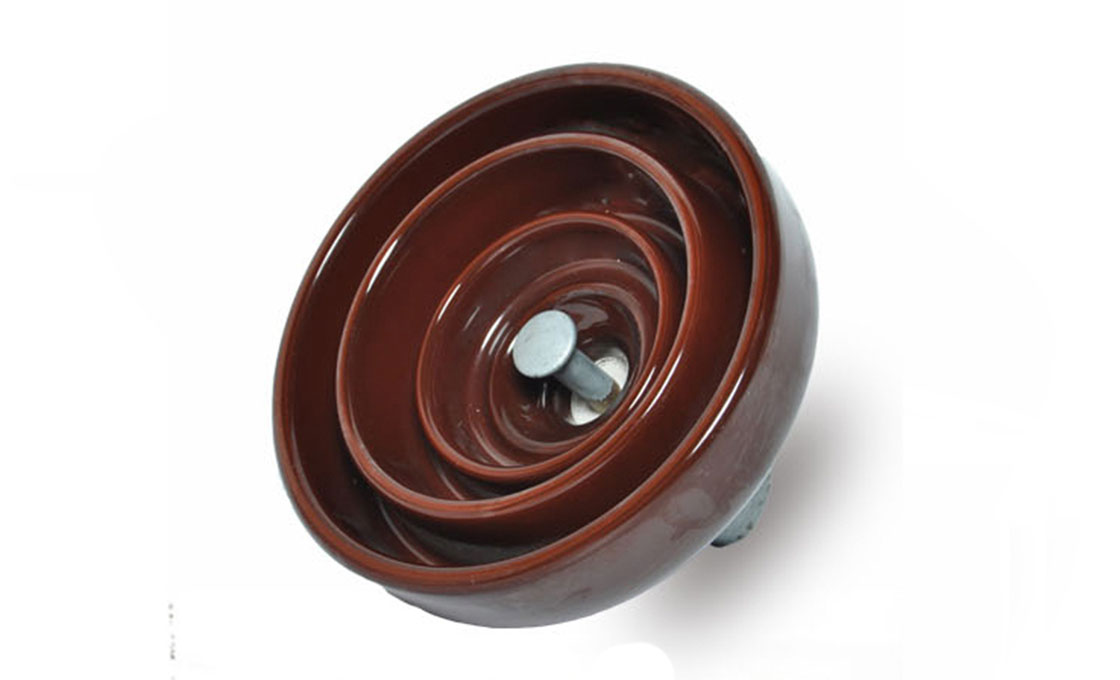
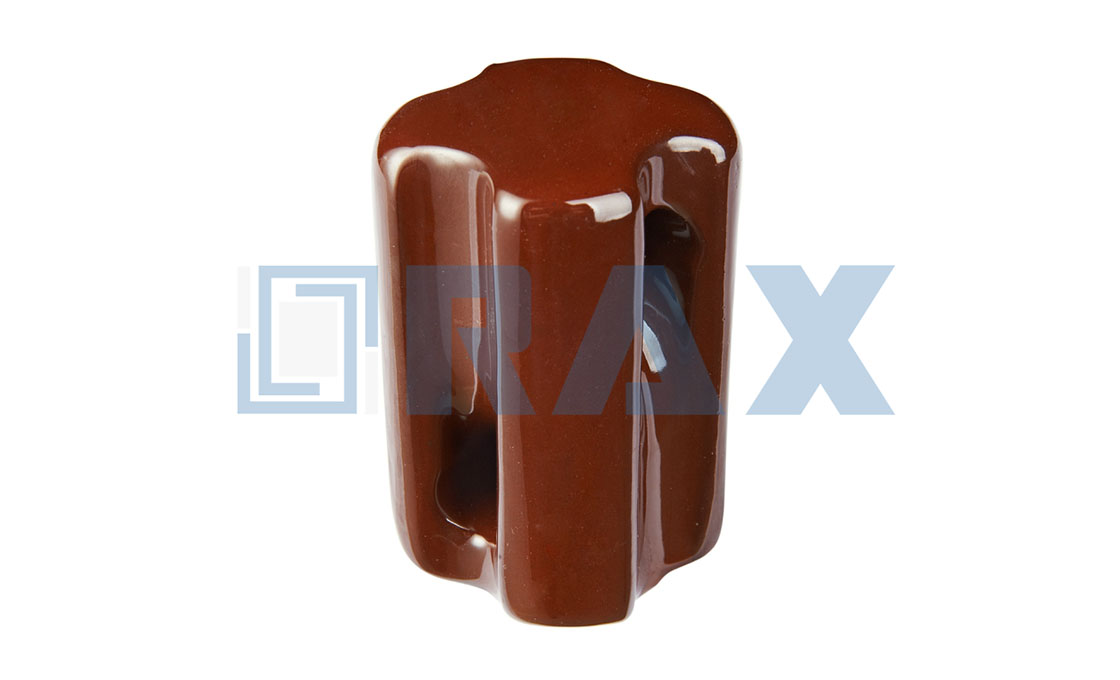
porcelain disc insulator
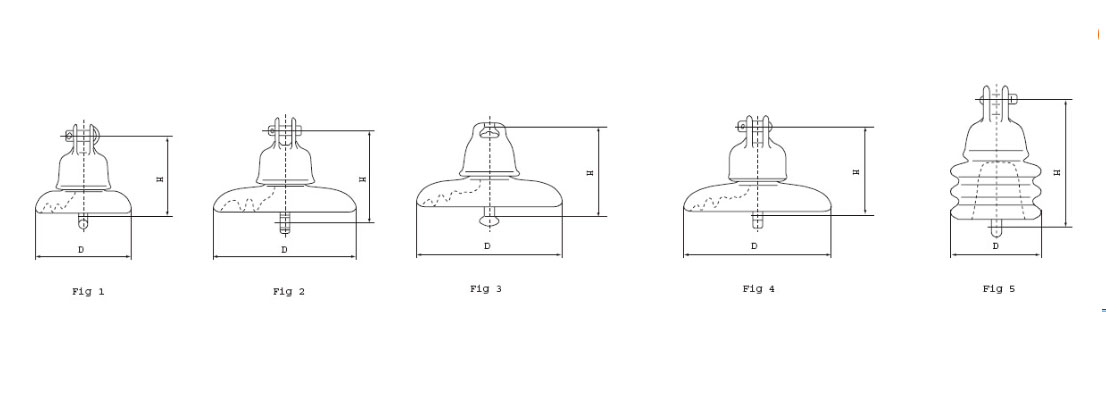
| Fig. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 5 | 1 | ||
| ANSI Class | 52-1 | 52-2 | 52-3 | 52-4 | 52-5 | 52-6 | 52-8 | 52-9 | 52-10 | ||
| Rated voltage (kv) | 11 | 11 | 33 | 33 | |||||||
| Main dimension(mm) | D | 165 | 190.5 | 254 | 254 | 254 | 254 | 254 | 108 | 280 | |
| H | 140 | 146 | 146 | 146 | 146 | 146 | 146 | 160 | 165 | ||
| Leakage distance (mm) | 178 | 210 | 292 | 292 | 292 | 292 | 320 | 171 | 280 | ||
| Power-frequency puncture voltage (kv) | 80 | 80 | 110 | 110 | 110 | 110 | 110 | 80 | 110 | ||
| Average flashover voltage | Power frequency | Dry (kv) | 60 | 65 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 60 | 80 |
| Wet (kv) | 30 | 35 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 30 | 50 | ||
| Critical impulsive wave | Positive (kv) | 100 | 115 | 125 | 125 | 125 | 125 | 125 | 125 | 100 | |
| Negative (kv) | 100 | 115 | 130 | 130 | 130 | 130 | 130 | 90 | 130 | ||
| Radio influence voltage | Test voltage to ground (kv) | 7.5 | 7.5 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 7.5 | 10 | |
| Max. RIV at 1000k Hz (μV) | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | ||
| Rated E & M failing load (kN) | 45 | 70 | 70 | 70 | 111 | 111 | 160 | 45 | 160 | ||
| Tension proof load (kN) | 22 | 35.5 | 35.5 | 35.5 | 55.5 | 55.5 | 80 | 22 | 80 | ||
| Impact strength (N·m) | 5 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 7 | 7 | 10 | 5 | 10 | ||
| Weight (kg) | 2.5 | 3.9 | 4.6 | 4.9 | 5.6 | 5.9 | 6.9 | 2.6 | 7.2 | ||
Porcelain suspension insulator details and parameters

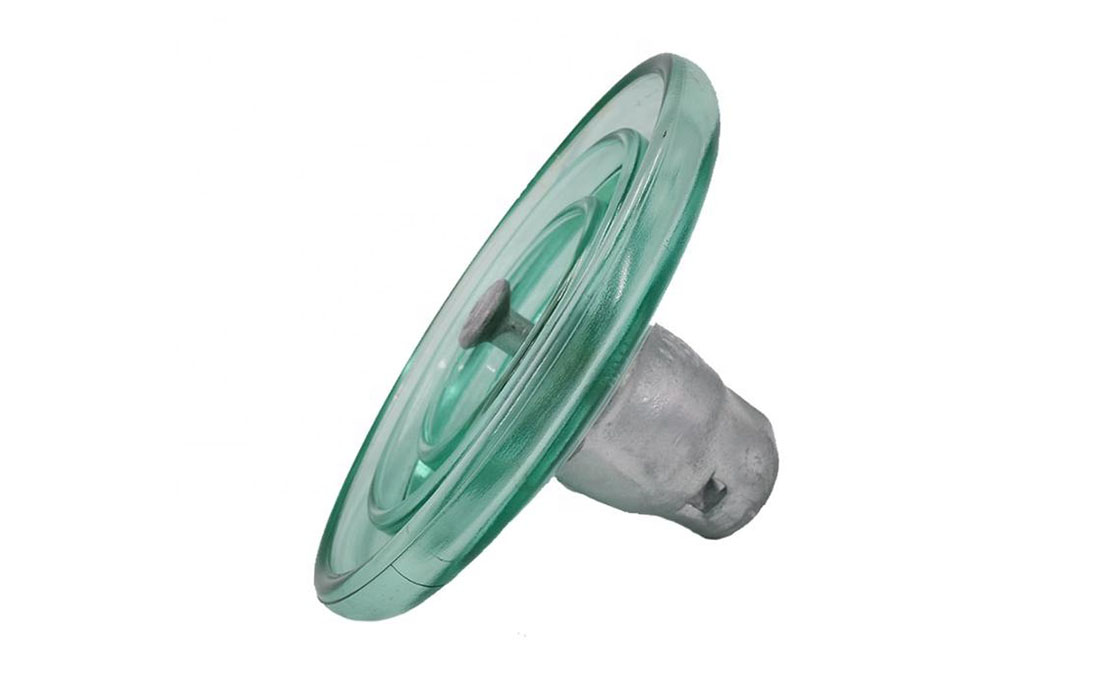
glass disc insulator
| Universal Model | U160B/170 | U160B/155 | U160B/146 |
| ( mm ) Diameter | 280 | 280 | 280 |
| ( mm ) Height | 170 | 155 | 146 |
| ( mm )Leakage distance | 400 | 400 | 400 |
| ( mm )Coupling | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| ( kN ) SML | 160 | 160 | 160 |
| ( kN )Tension Load Test | 80 | 80 | 80 |
| ( kV )Power frequency Withstand wet | 45 | 45 | 45 |
| ( kV )Lightning Impulse Withstand | 110 | 110 | 110 |
| ( P.U )Puncture Impulse Voltage | 2.8 | 2.8 | 2.8 |
| ( kV )Puncture power frequency voltage | 130 | 130 | 130 |
Glass suspension insulator details and parameters
Suspension Insulator: The Complete Guide
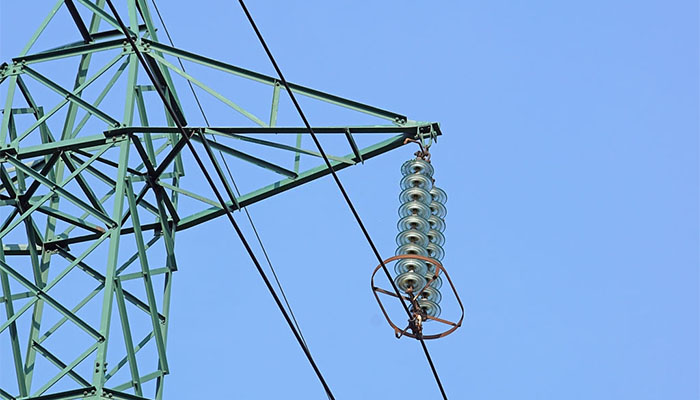 In electricity and electronics, insulators are used for blocking the flow of electric current to the undesired sections or even directions. If many conductors are close to each other, the insulator does the work of isolating them. This prevents cases of short-circuiting.
In electricity and electronics, insulators are used for blocking the flow of electric current to the undesired sections or even directions. If many conductors are close to each other, the insulator does the work of isolating them. This prevents cases of short-circuiting.
In the overhead transmission lines, insulators are used for preventing the leakage of the electric current. Keep in mind that poles and towers support these transmission lines. There are different types of insulators for transmission lines. They include strain insulator, pin insulator suspension insulator, among others.
In this guide, our focus will be on suspension insulators. I will guide you about it and how you should choose the right suspension insulator for the project.
What is a suspension insulator?
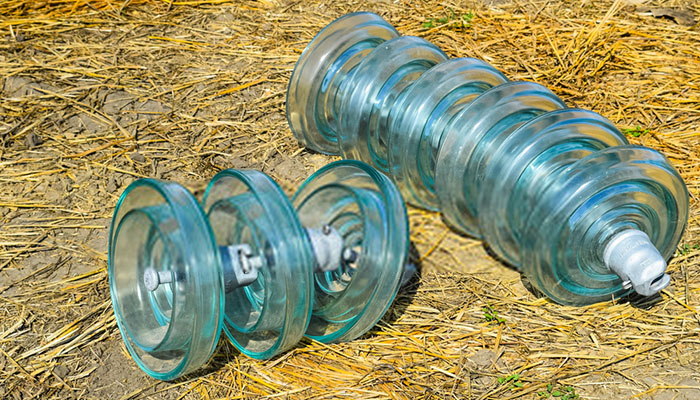 A suspension insulator, which is also known as a strain insulator, is a type of insulator designed to protect the overhead power line. The insulating materials for this insulator comprise discs connected to each other by string-like metal links.
A suspension insulator, which is also known as a strain insulator, is a type of insulator designed to protect the overhead power line. The insulating materials for this insulator comprise discs connected to each other by string-like metal links.
The transmission line conductor is suspended at the bottom side of the suspension string, which connects directly to the pole or tower.
Here are different insulation materials that are used on the suspension insulators. They include porcelain, glass, polymer, ceramic, and crystals such as quartz.
The main difference between pin insulator and suspension type insulator is their insulation capacity. Suspension insulator is ideal for transmission lines with more than 33Kv. The transmission line voltage will dictate the number of discs to be used on the suspension insulator.
The ability to overcome the pin insulator’s limitation capacity is the main reason why suspension insulators are preferred for most transmission lines. Of course, you have to keep in mind all other technical and non-technical factors before deciding whether to use a pin insulator or suspension insulator.
How does a suspension insulator work?
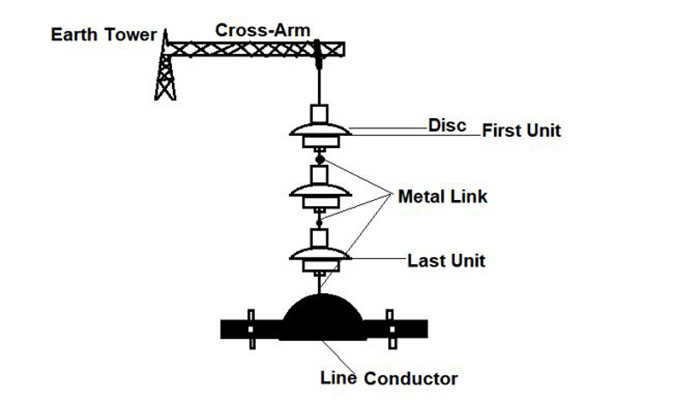 A suspension insulator for an overhead powerline comprises two major components. These are the cross-arms and the disc insulators, which are coupled up by metallic links. These suspension insulator parts work as a system to protect the transmission line.
A suspension insulator for an overhead powerline comprises two major components. These are the cross-arms and the disc insulators, which are coupled up by metallic links. These suspension insulator parts work as a system to protect the transmission line.
A complete set of suspension insulator is manufactured by stringing the disc insulators using the metallic string. The connection of the insulators is in series.
For the pole lines where the conductor is suspended from the insulator’s bottom section, cross-arms are used for securing the insulator in place. The cross-arm also guarantees the stability of the insulator.
Each disc for a suspension insulator is designed to have a low voltage. For example, a single disc of the insulator can be calibrated to have 11 kV. The discs are connected in series, and the desired voltage will determine the number of discs to be used on the insulator.
The series connection of the insulation of the discs provides maximum independence of the insulator. This is to say that the performance of one disc does not depend on the others. In the event that one disc fails, the rest will remain unaffected.
Types of suspension insulators
Suspension type insulators are grouped into different categories. In terms of the design, the insulator can be a cap-and-pin type or an interlink suspension insulator.
The cap and the pin type insulator comprises a forged steel cap and a galvanized steel connected to a porcelain material. A ball clevis and a socket are used to complete the connection.
On the other hand, an interlink type insulator comprises two curved sections that are joined together at an angle of 90 degrees.
In terms of the insulating material, suspension type insulators are divided into composite suspension insulator, porcelain suspension insulator, polymer suspension insulators, and glass suspension insulators.
When choosing the types of suspension insulators, it is important to analyze your requirements and know the type that will work for your application.
Advantages of suspension insulators
If you are pondering on whether to buy suspension insulators or not, here are some of the reasons that can convince you to go ahead with that move:
-The insulator is suitable for high-voltage transmission lines. Unlike the pin insulator, whose maximum capacity is 33kV, suspension insulator can provide insulation for the transmission lines that are rated more than 33kV.
-The insulator is very versatile. Even though the suspension insulator is applicable for the high voltage transmission lines, you can still use it on the low voltage conductors. It is also possible to increase the insulating capacity of the insulator if there is an increase in voltage. It would be best if you bought extra insulation discs.
-Highly flexible: Once installed, suspension insulators do not remain rigid or transfixed at the same position. They are allowed to swing so as to cope with the ever-changing conditions. The flexibility minimizes the mechanical stress on the insulator hence lengthening their service life.
-Easy to maintain: Suspension insulators are made of strong materials that can last for a long time. It is also easy to replace the insulation disc in case they get damaged. You will focus on the affected disc without touching the others.
Despite the advantages, suspension type insulator also has some drawbacks. It tends to increase the spacing distance between the conductor. Also, the insulator is more expensive than the pin insulator. However, it still remains to be a viable investment for the transmission line.
Applications of suspension insulators
Suspension insulator tool is used on both the high-voltage and low voltage transmission lines. Some of the applications include:
- Electric poles
- Generators
- Transformers
- Railway lines
- Electric motors
Are there other applications that you think deserve to be on this list? Talk to the suspension insulator manufacturers. They are capable of customizing the product to meet your specific power line needs.
Suspension Insulator Manufacturer in China: Powertelcom
 Are you looking for the best suspension isolators for sale? Where you buy the insulator matters. Once you are sure about the insulator’s specifications, you should go ahead and look for reliable suspension insulator manufacturers and suppliers in China.
Are you looking for the best suspension isolators for sale? Where you buy the insulator matters. Once you are sure about the insulator’s specifications, you should go ahead and look for reliable suspension insulator manufacturers and suppliers in China.
For this reason, we at Powertelcom are dedicated to manufacturing and selling this power line accessory. We are a global manufacturer of suspension insulators in China. We design, manufacture, and supply this product.
We have years of experience in this field, which explains why we are experts in this field. We are always eager to meet the needs of our customers. In case you would like to know about the suspension insulator price or any other information concerning the product, don’t hesitate to contact us.
FAQ
What is a suspension insulator?
Just the same as the string insulator, a suspension insulator is a flexible insulator string that consists of some disc insulators connected with each other by metal connections. It is mounted in the vertical position of the transmission lines.
What are the types of the suspension insulators?
There are two types of suspension insulators: cap and pin insulator and interlink insulator (also known as Hewlett type insulator). They are made of porcelain or glass.
How does a suspension insulator work?
A suspension insulator for an overhead line comprises two major components. These are the cross-arms and the disc insulators, which are coupled up by metallic links. These suspension insulator parts work as a system to protect the transmission line.
For the pole lines where the conductor is suspended from the insulator’s bottom section, cross-arms are used for securing the insulator in place.
What are the advantages of suspension insulators?
- Suitable for high voltage transmission lines.
- Very versatile. The number of discs can be changed.
- Highly flexible: They are allowed to swing so as to cope with the ever-changing conditions.
- Easy to maintain and easy to replace the insulation disc in case they get damaged.










