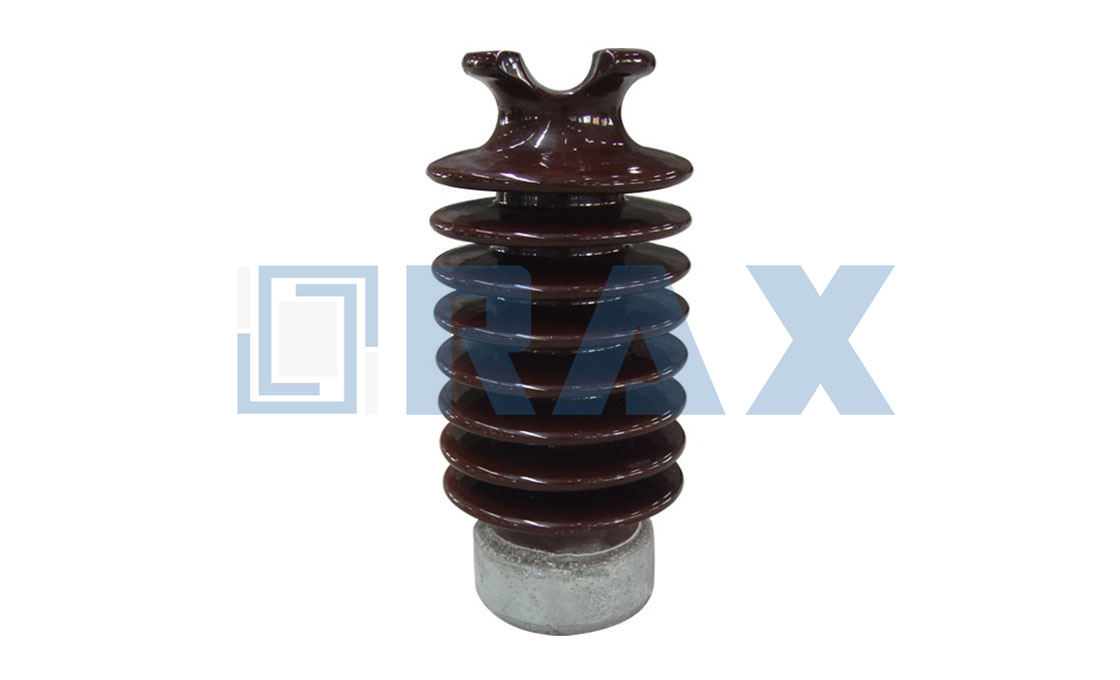
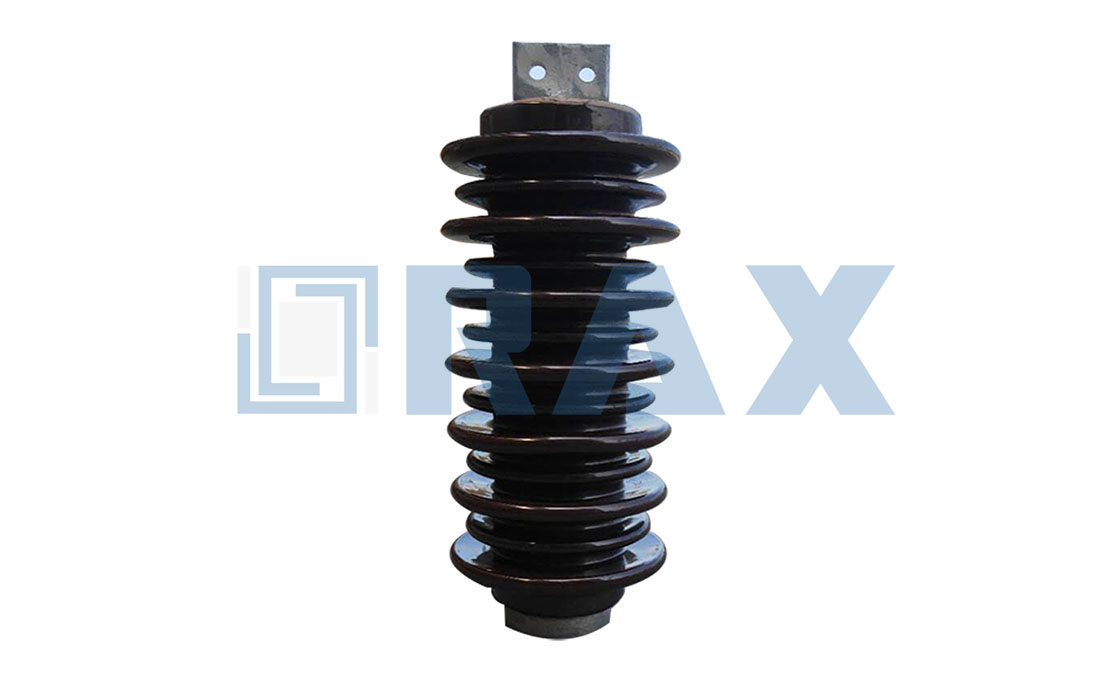
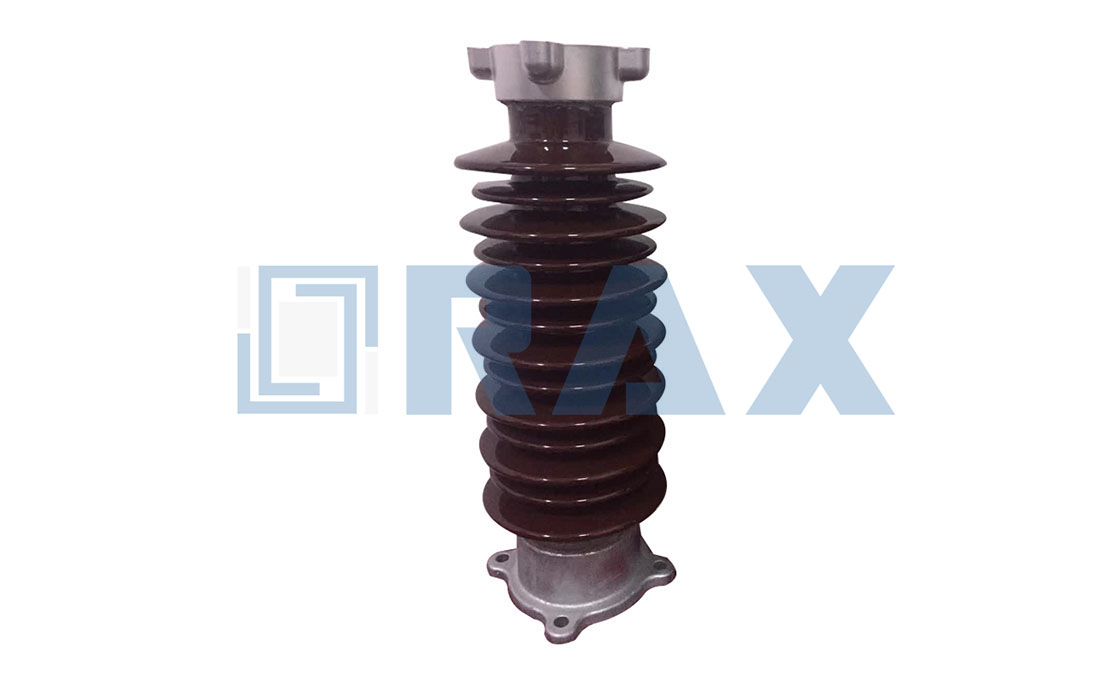
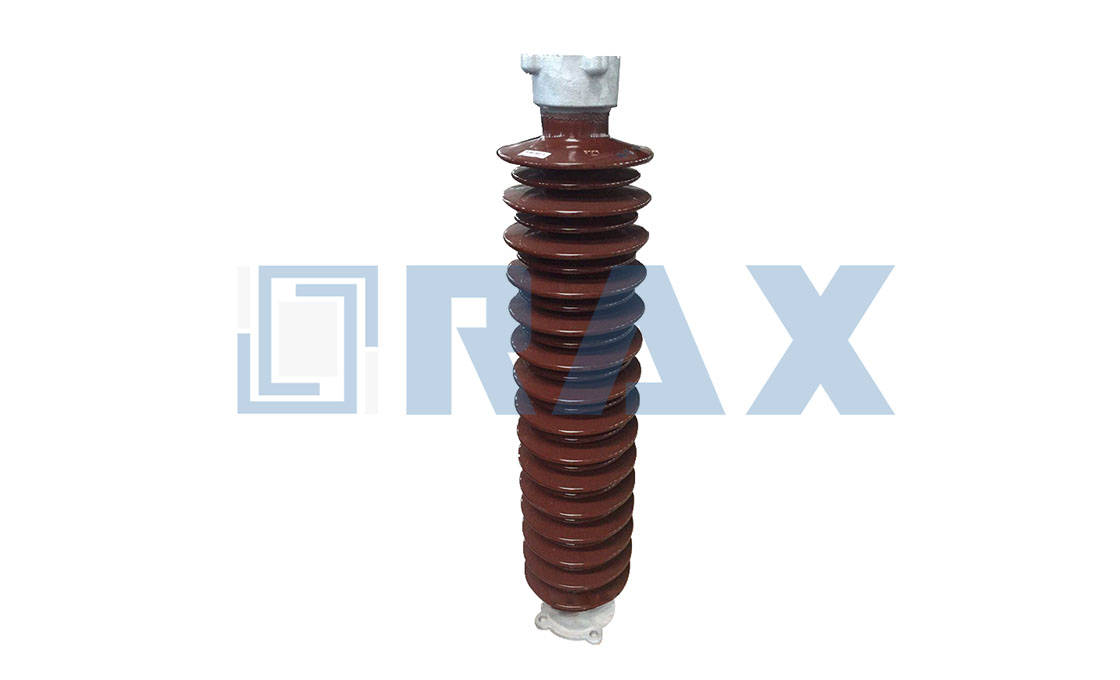
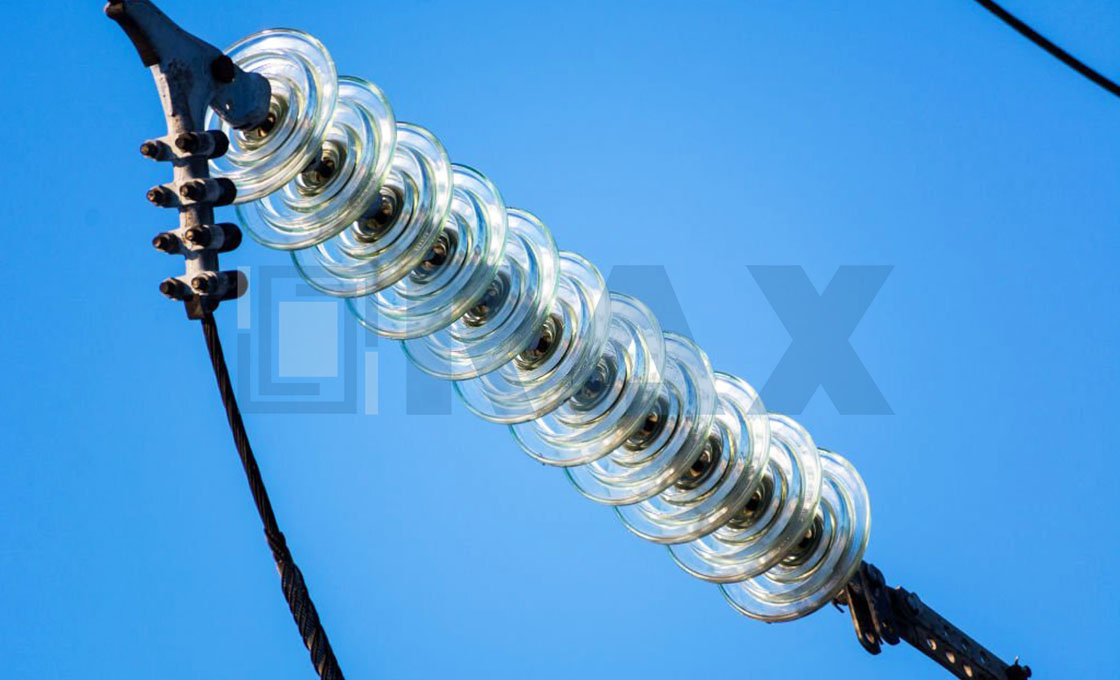
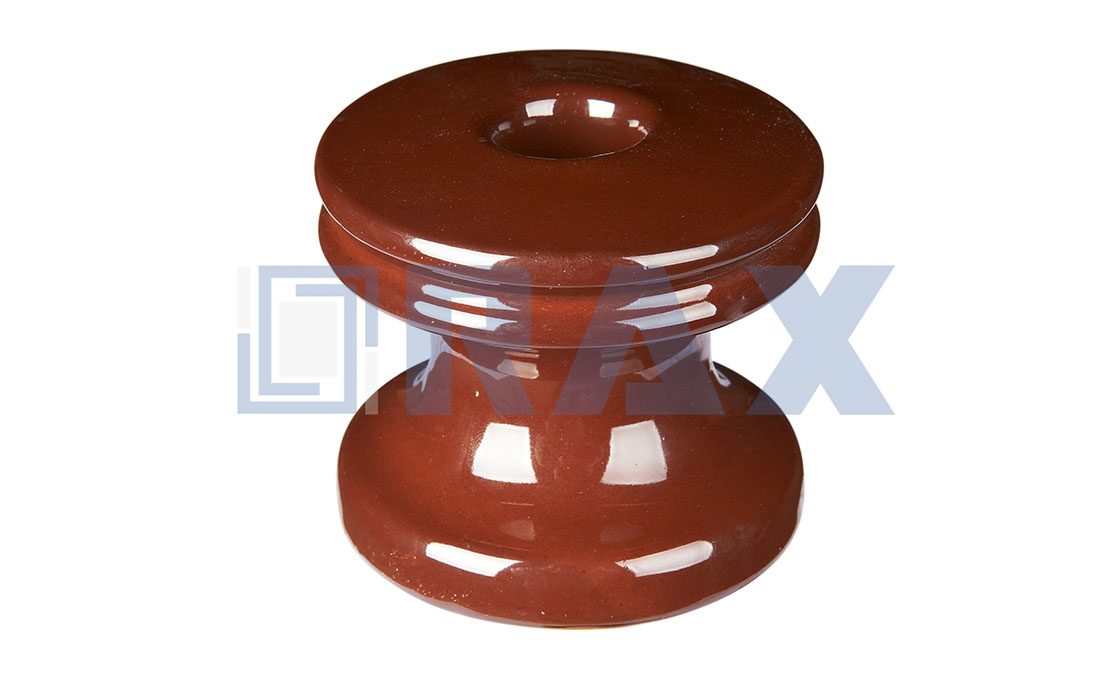
Post Insulator
Post insulator is a type of high voltage (HV) insulator designed according to IEC, ANSI, and other standards, they are used in power systems up to 1100 kV.
The post insulator is made of one piece of porcelain or composite material (silicone rubber). Due to the excellent mechanical properties, the post insulator is widely used in different applications.
In the distribution and transmission line, the post insulator is also named line post insulator.
According to the designs, there are 5 types of line post insulators: tie top line posts, vertical clamp top line posts, horizontal (stud mount) clamp top line posts, horizontal (gain base) line posts, and brace post insulators.
When used as a tie top line post on power lines up to 69 kV, it is fixed to the conductors by a top tie and replaces traditional pin insulators.
There is a clamp unit at the end of the insulator for fixing the other 4 types. Line post insulator supporting conductors can be mounted on the utility pole horizontally as well as vertically.
In substations and related applications, the post insulator is also called a station post insulator. The station post is commonly mounted in a vertical position to protect transformers, switchgear, and other related components. It is subjected to bending and compression forces in service. Two or more insulators can be assembled together for higher voltage applications.
As a responsible electrical insulator manufacturer, Rax Industry team will try our best to make your business take off. Welcome to send us an inquiry now.
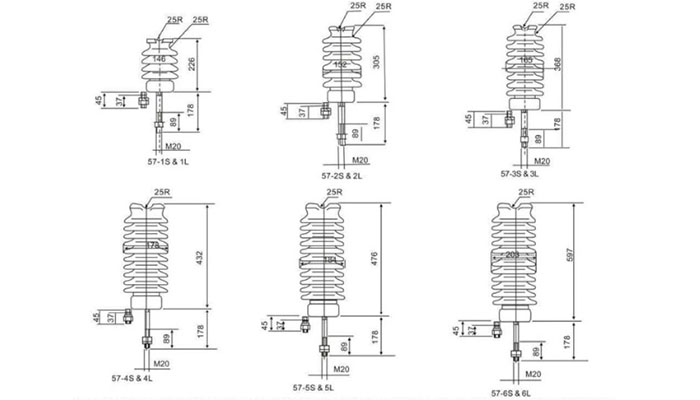
typical line post insulator drawing
| ANSI CLASS | 57-1 | 57-2 | 57-3 | 57-4 | 57-5 | ||
| Creep Age Distance (mm) | 356 | 559 | 737 | 1016 | 1143 | ||
| Dry Arcing Distance (mm) | 165 | 241 | 311 | 368 | 430 | ||
| Cantilever Strength (kn) | 12.5 | 12.5 | 12.5 | 12.5 | 12.5 | ||
| Flashover Voltage kV | Power Frequency
| Dry | 70 | 100 | 125 | 140 | 160 |
| Wet | 50 | 70 | 95 | 110 | 130 | ||
| Critical Impulse | Positive (kV) | 120 | 160 | 200 | 230 | 265 | |
| Negative (kV) | 155 | 205 | 260 | 340 | 380 | ||
| Radio Influence Voltage | Test Spanning to the ground (kV) | 15 | 22 | 30 | 44 | 44 | |
| Maximum RIV at 1000kHz (uv) | 8000 | 12000 | 16000 | 16000 | 25000 | ||
| 100 | 100 | 200 | 200 | 200 | |||
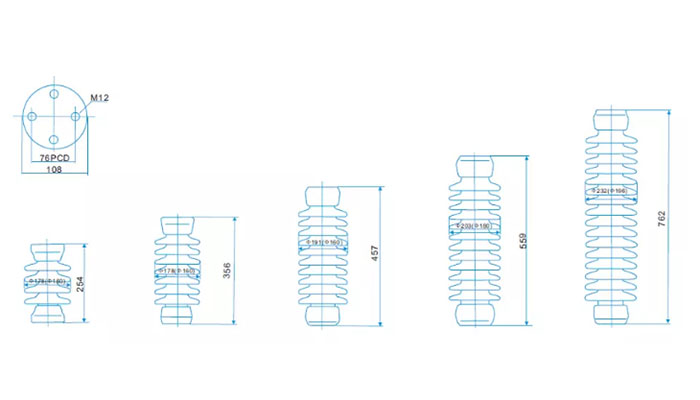
station post insulator drawing
| ANSI CLASS | TR205 | TR208 | TR210 | TR214 | TR216 | ||
| Creep Age Distance (mm) | 394 | 610 | 940 | 1092 | 1892 | ||
| Tensile Strength (kn) | 38 | 44.5 | 53 | 62 | 71 | ||
| Compression Strength (kn) | 44.5 | 44.5 | 66.7 | 66.7 | 111 | ||
| Cantilever Strength (kn) | 8.9 | 8.9 | 8.9 | 8.9 | 6.7 | ||
|
Flashover Spanning | Power Frequency | Dry | 85 | 110 | 145 | 170 | 235 |
| Wet | 55 | 75 | 100 | 125 | 180 | ||
| Critical Impulse | Positive (kV) | 125 | 170 | 225 | 280 | 390 | |
| Negative (kV) | 200 | 250 | 290 | 340 | 475 | ||
| Impulse Withstand Voltage (kV) | 110 | 150 | 200 | 250 | 300 | ||
| Low-Frequency Withstand Voltage | Dry(kV) | 55 | 75 | 100 | 125 | 180 | |
| Wet(kV) | 40 | 60 | 80 | 100 | 145 | ||
Post Insulators in Overhead Lines: The Complete Guide
Post insulators can be used in both transmission lines and substation systems. In this post, we mainly talk about post insulators in transmission lines.
A complete transmission line should have insulators. These are devices that are used for supporting conductors at different positions on the line. The fact that they are insulators means that no electric current will flow through them. This allows the insulator to provide maximum support without compromising the transmission of current or even the safety of the pole line.
One of the common transmission line insulators is the post insulator. Are you seeking to buy the best post insulators in China? Read on as we reveal everything that you should know about these transmission line accessories and how to choose one.
- 1. What is a Post Insulator?
- 2. What are the types of post insulators?
- 3. What is the difference between Pin Insulators and Post Insulators?
- 4. Typical Features of Post Insulators
- 5. Post Insulators Strength Ratings
- 6. Installation and Maintenance of Post Insulators
- 7. Post Insulator Manufacturers
- 8. Frequently asked questions (FAQ)
What is a Post Insulator?
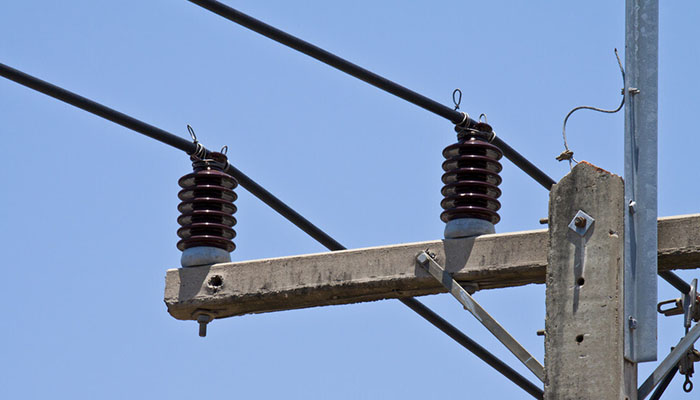 In transmission lines, post insulators are also called line post insulators. The flanges of this insulator are sharp and narrow. This design facilitates a creepage distance that will counter the problem of electrode pollution.
In transmission lines, post insulators are also called line post insulators. The flanges of this insulator are sharp and narrow. This design facilitates a creepage distance that will counter the problem of electrode pollution.
Most post insulators are made of ceramic materials even though composite post insulators are quite comm. Composite post insulator types are usually tested based on the quality of each material.
The choice of the material should meet both the mechanical and electrical properties of an insulator.
What are the types of post insulators?
 Top end fittings and bottom end fittings are different between types of line posts. According to the designs, there are mainly 5 types of line post insulators:
Top end fittings and bottom end fittings are different between types of line posts. According to the designs, there are mainly 5 types of line post insulators:
Tie top line posts: Also called core rod F neck line posts, they are technically similar to pin insulators.
Vertical clamp top line posts: With a clamp top and a stud base, it is mounted on the top of a utility pole.
Horizontal (stud mount) clamp top line posts: When a vertical clamp top line post mounted on the side of a utility pole, it is called a horizontal (stud mount) clamp top line post.
Horizontal (gain base) line posts: With a clamp top and a gain base, it is usually mounted on the side of a pole.
Brace post insulators: A special combination of a horizontal line post and a suspension insulator, which is made of silicon rubber.
What is the difference between Pin Insulators and Post Insulators?
When buying a post insulator, you are likely to confuse it with a pin insulator. They tend to look the same even though they are different products.
The main difference with pin insulators is application areas. Post insulators are best suited for the higher voltage transmission lines.
There are many other differences that we are going to highlight.
The table below shows the differences:
| Pin Insulator | Post Insulator |
| Suitable for the 33kV transmission lines | Suitable for both low voltage and high transmission lines of up to 150kV |
| It has a single stag | Can have a single stag and as well as multiple stags |
| Two pin insulators cannot be installed together for high voltage applications | You can use two or more post insulators, one above the other for high-voltage applications |
| The installation of the conductor is through binding | A connector clamp is used to fix the conductor on top of the insulator |
| The metallic arrangement is provided only at the bottom section of the insulator | The metallic arrangement is available both at the top and bottom of the insulator |
Typical Features of Post Insulators
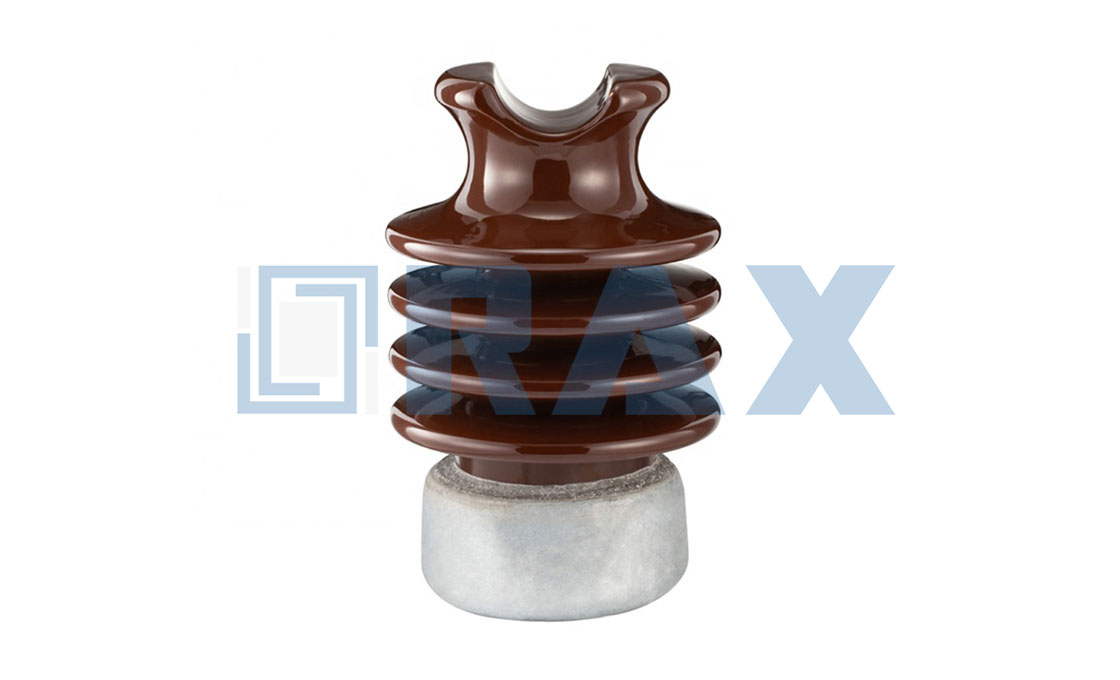 What makes post insulators ideal for their roles on the transmission lines? The specific properties of post insulators include:
What makes post insulators ideal for their roles on the transmission lines? The specific properties of post insulators include:
-High mechanical strength: Post insulators are subjected to bending, compression, and torsion forces. The insulator must have high mechanical strength to overcome these forces. Otherwise, it would easily break and cost more to replace.
-Solid and puncture-proof: Being exposed to all vagaries of nature can put the insulator at risk of being damaged due to punctures.
-Made of porcelain and aluminum oxide ceramic: The material for making the insulator should not only be strong enough but also should be a pure insulator. This is why aluminum oxide ceramic is used as it ranks fairly well in terms of insulating properties.
Porcelain is also a perfect insulator not underscoring its immense strength.
-Flexible creepage distance: The post insulator should have a proper creepage distance that will not compromise the integrity of the insulating path. This distance protects against tracking.
Before you buy post insulators, check to verify that they meet the relevant global standards.
Like other transmission line accessories, the design and make of post insulators should meet the minimum standards for IEEE, IEC, and NEMA. These standards define the quality of the insulator.
This is just one of the many reasons why we insist that you buy from reputable post insulator manufacturers in China. Most of them make insulators that meet the minimum global standards.
Post Insulators Strength Ratings
Post insulators for transmission lines come with different strength ratings. The standard ratings for post insulators are used in all applications(high-voltage and bus applications).
The standard strength post insulators are designed to meet all the ANSI standards for mechanical and electrical properties for their respective voltage classes.
They are the most common type of post insulators that you are likely to find in the market. The 22kV post insulator and 33kV post insulator belong to this category
High strength post insulators tend to have an extra amount of mechanical strength. They are suitable for heavy-duty bus b applications and switch transmission lines.
However, these porcelain post insulators have the same electrical strength as the standard strength post insulators.
High strength post insulators are also suitable for applications that tend to experience severe short circuits.
Under this category, you should consider getting a 69kv post insulator.
Extra-high strength post insulators are mainly used for transmission projects that require extremely heavy mechanical loads. These insulators can either meet or exceed the ANSI standards both in terms of the electrical and mechanical properties.
A 115 kV post insulator and the 150 kv post insulator belong to this group
Installation and Maintenance of Post Insulators
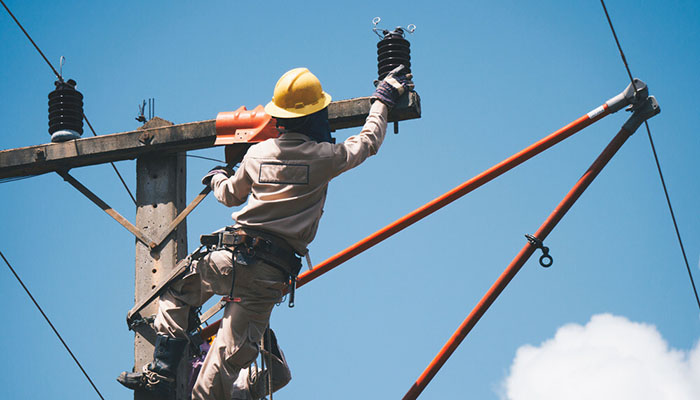 In most cases, post insulators are installed to assume a vertical position. However, there are some applications where the insulators are installed horizontally.
In most cases, post insulators are installed to assume a vertical position. However, there are some applications where the insulators are installed horizontally.
For the horizontal application, must be reduced by 50% of the total weight of the unit. This means that if the post insulator is rated 2000 Ibs, the most recommended working load should be 1000 Ibs.
Post insulators for powerline require minimum coating thanks to their exterior surface coating. It keeps dirt and other impurities from the insulator hence protecting it from chemical and physical damage.
The hot-dip galvanized metal fillings at the end of the porcelain guarantees maximum protection.
Post Insulator Manufacturer
By now you may be wondering about where to buy post insulators for power transmission lines. The surest place to get this insulator is from a reliable post insulators manufacturer in China.
The important role that a post insulator plays on an overhead transmission line requires that you buy a reliable insulator. This is something that will not fail when in operation.
At Powertelcom, we design and manufacture quality post insulators that meet all the global standards. We are ranked among the best post insulator manufacturers in China.
Would you want to know the post insulator prices, designs, or specifications? Contact us and we will avail all the information that you need.
FAQ
What is a post Insulator?
Post insulator is a type of high voltage (HV) insulator designed according to IEC, ANSI, and other standards, they are used in power system up to 1100 kV.
Where is the post insulator used?
Post insulator can be used in either transmission lines or substations,
The post insulator used in the transmission lines is also named line post insulator, and called station post insulator or bus post insulator in the substations.
What are typical features of post insulators?
- High mechanical strength.
- Solid and puncture-proof.
- Made of porcelain or composite material.
- Flexible creepage distance
What is the main difference between post insulators and pin insulators?
The main difference with pin insulator is application areas. Post insulators are best suited for the higher voltage transmission lines.
What tests should do with post insulators?
- Routine Tests: Electrical Routine tests, Mechanical Routine tests, Visual examination and check for compliance.
- Sample Tests, insulators took at random from batches should take Verification of dimensions, Temperature cycle test, mechanical failing load test, and so on.
- Type Tests, thermal mechanical performance tests:
- Dry lightning impulse and Wet power frequency withstand voltage test.
All the tests are performed in accordance with the relevant standards supplemented by the specific requirements.










