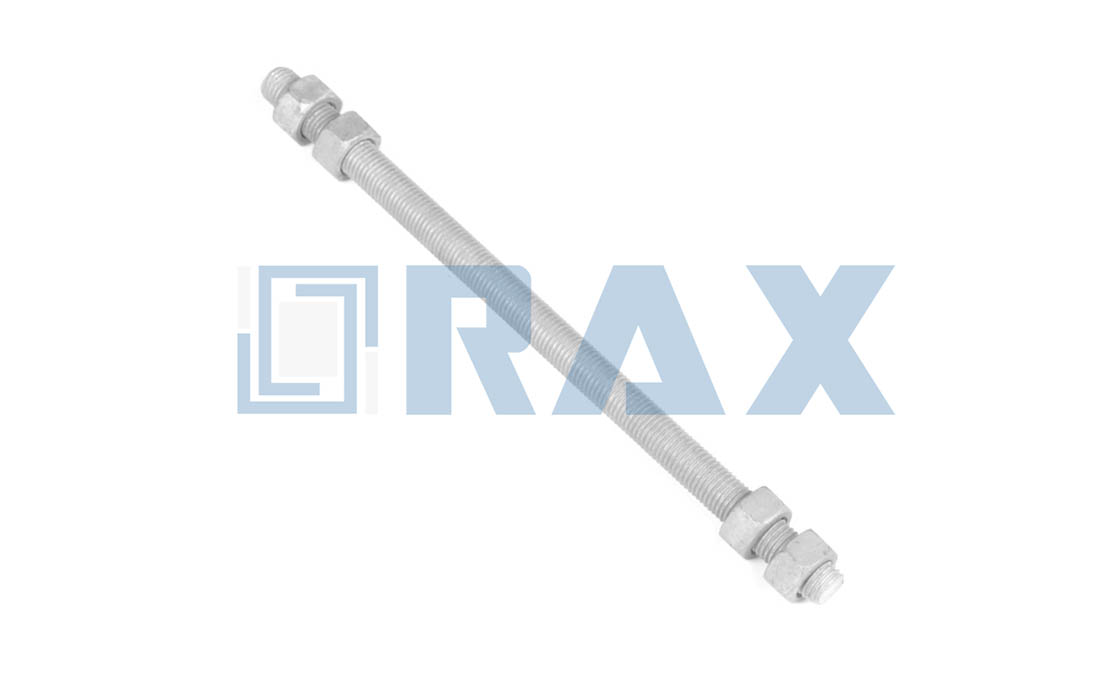
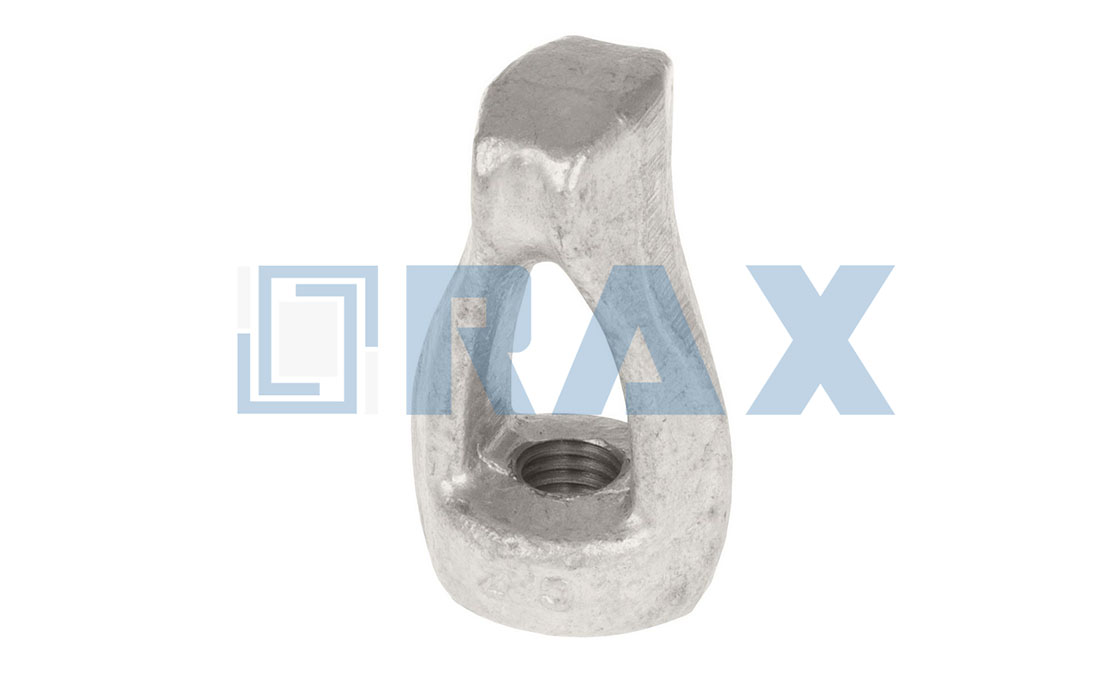
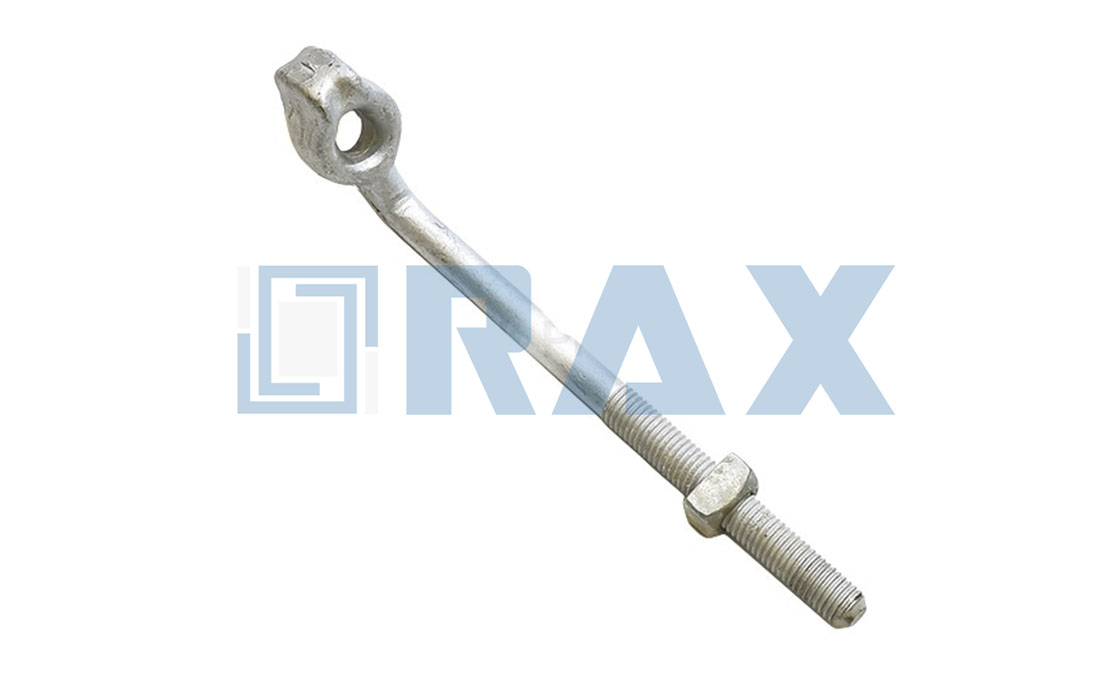
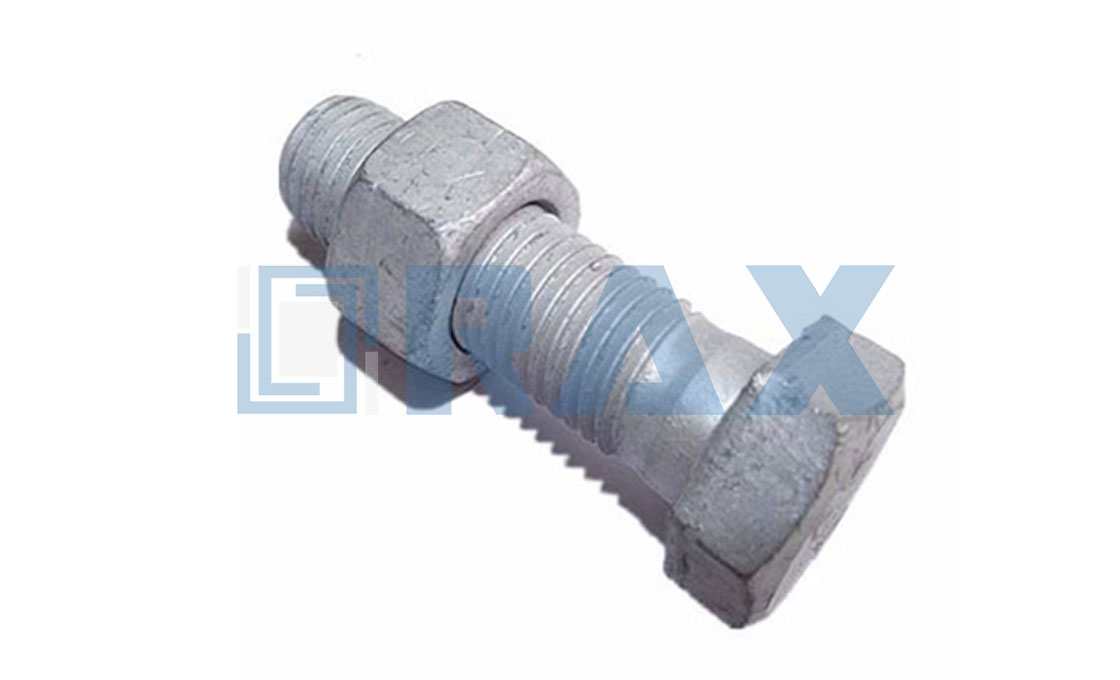
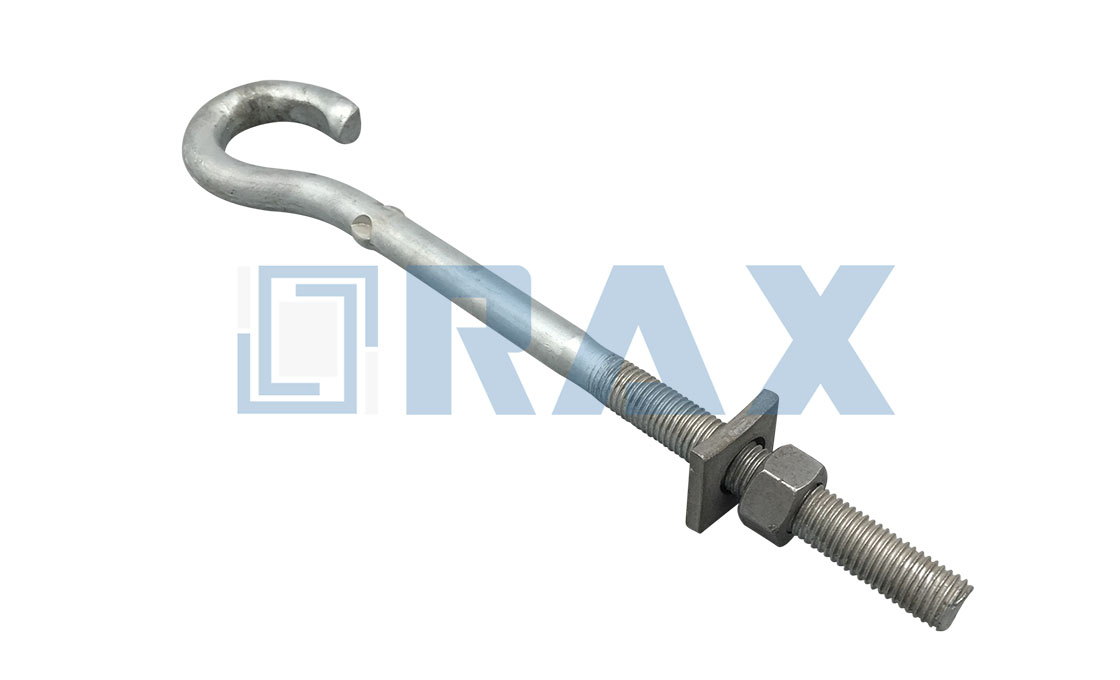
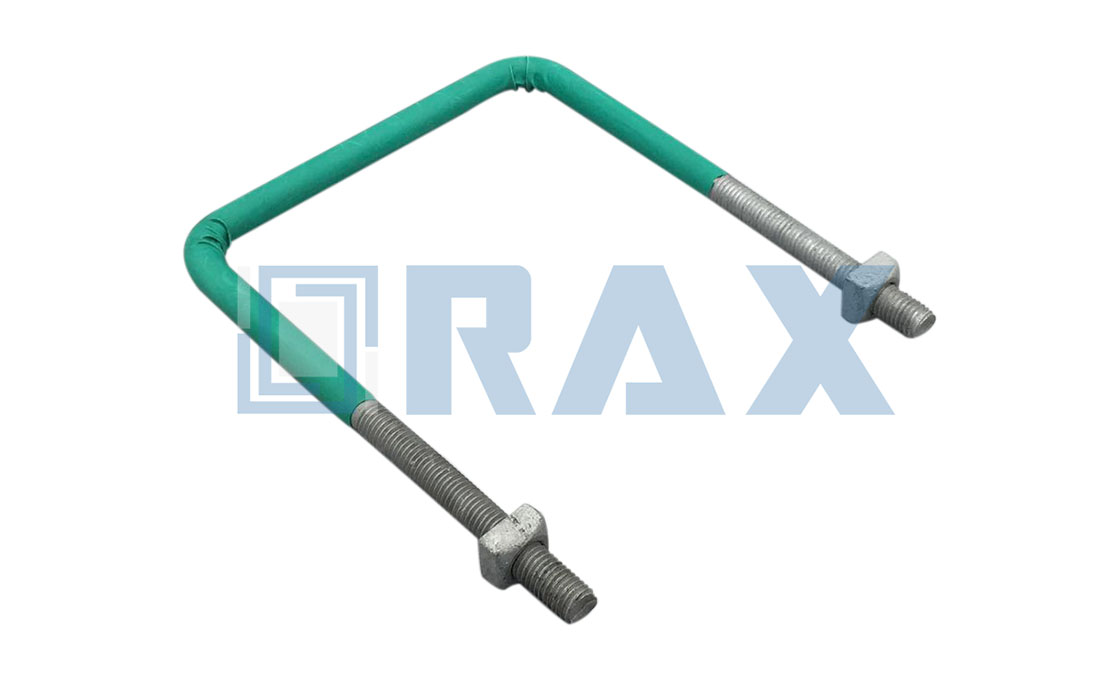
Upset Bolt
The upset bolt is a type of fastener designed for the spool insulator, it is assembled on one side-pole to support the neutral conductors or power wire. An upset bolt is also called an upset spool bolt or bolt upset.
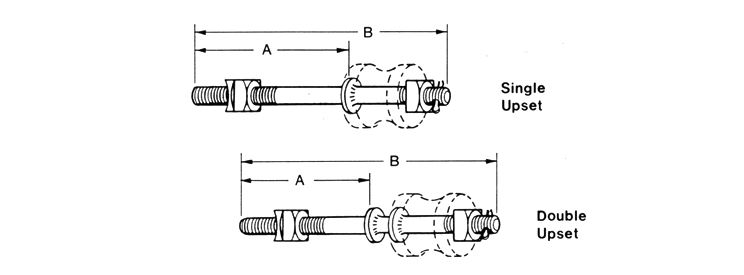
There are two types of upset bolts, single upset bolts, and double upset bolts. The difference between the single upset and double upset is the number of the forged plates at the insulator end.
The insulator pin goes across one end of the thread. The forged plate will stop the insulator pin from moving down. In this way, the insulator pin is fixed on the end of the upset bolt to insulate the conductor and secondary service wires. The upset bolt thread diameter is 5/8‘’
There is a hole at end of the upset bolt with a steel pin to help stop the insulator pin from coming out. The finished is hot-dip galvanized ASTM A-153. The main function of the spool bolt is to support the insulator pin for conductors and power wires going through.
Rax Industry upset bolt is a screw head type bolt with 2 regular square nuts, 1 lock nut, and 1 round washer.
As a professional manufacturer, supplier, and exporter, Rax Industry can support all sizes of upset bolts, We can also customize them according to your designs.
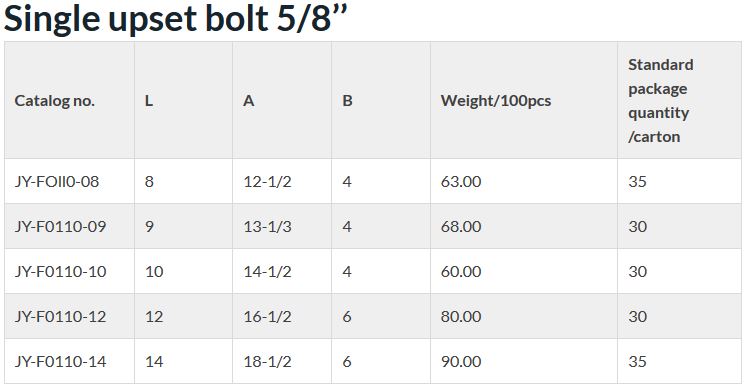
Single upset bolt 5/8’’
| Catalog no. | L | A | B | Weight/100pcs | Standard package quantity /carton |
| JY-FOll0-08 | 8 | 12-1/2 | 4 | 63.00 | 35 |
| JY-F0110-09 | 9 | 13-1/3 | 4 | 68.00 | 30 |
| JY-F0110-10 | 10 | 14-1/2 | 4 | 60.00 | 30 |
| JY-F0110-12 | 12 | 16-1/2 | 6 | 80.00 | 30 |
| JY-F0110-14 | 14 | 18-1/2 | 6 | 90.00 | 35 |
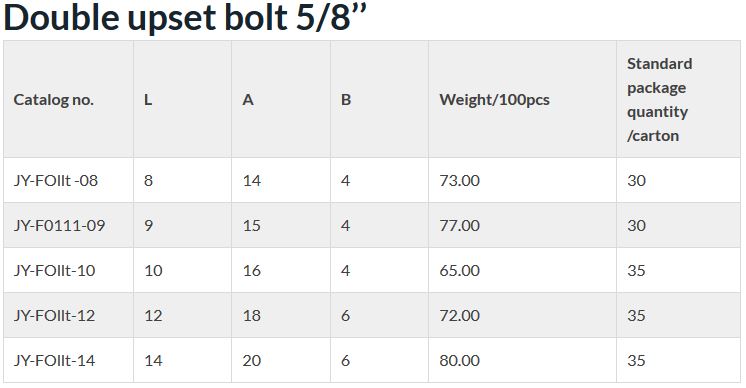
Double upset bolt 5/8’’
| Catalog no. | L | A | B | Weight/100pcs | Standard package quantity /carton |
| JY-FOllt -08 | 8 | 14 | 4 | 73.00 | 30 |
| JY-F0111-09 | 9 | 15 | 4 | 77.00 | 30 |
| JY-FOllt-10 | 10 | 16 | 4 | 65.00 | 35 |
| JY-FOllt-12 | 12 | 18 | 6 | 72.00 | 35 |
| JY-FOllt-14 | 14 | 20 | 6 | 80.00 | 35 |
Upset Bolts: The Ultimate Guide
In the event of looking for a fastener, you will come across a number of bolts that perform different functions.
Among them is the upset bolt which is a unique type of bolt you might not have heard of before.
Well, wonder no more as I will take you through the details you need to know about the upset bolt.
- Chapter 1: What is an Upset Bolt?
- Chapter 2: Types of Upset Bolts
- Chapter 3: Main Applications of Upset Bolts
- Chapter 4: Parts of Upset Bolts
- Chapter 5: Technical Specifications of Upset Bolts
- Chapter 6: Manufacturing Process of Upset Bolts
- Chapter 7: Installation of Upset Bolts
- Chapter 8: Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Chapter 9: Conclusion
What is an Upset Bolt?
There are a number of synonyms you will come across as you read about the upset bolt.
The names are bolt upset or spool bolt which means the same thing as an upset bolt.
 Upset bolt
Upset bolt
The design of the upset bolt is to assemble on one side and support the power wire and neutral conductors.
It has an insulator pin that will go across one particular end of the threads on the upset bolt.
Apart from that, there is a forged plate that will prevent the pin from falling down.
The insulator pin on the end of the upset bolt insulates the secondary service wire and the conductor.
Apart from that, the upset bolt has a hole at the end which protects the insulator pin from coming out.
The hole has a steel pin which will also aid in preventing the insulator pin from falling.
It is a type of a screw head bolt consisting of a lock nut, round washer, and two regular square nuts.
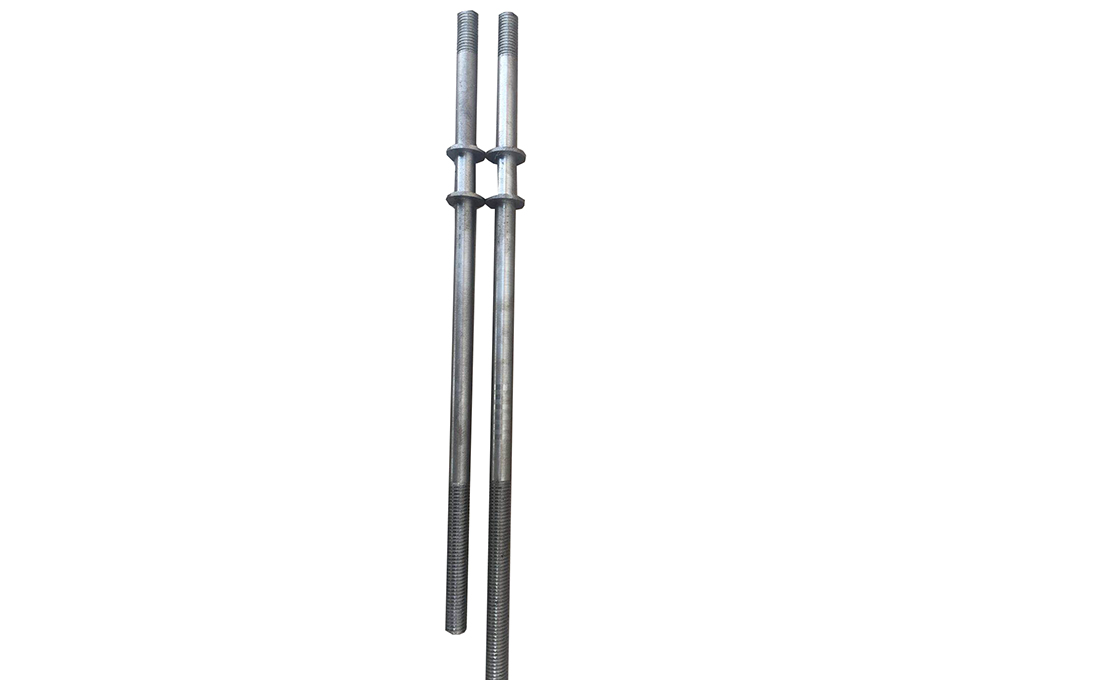
Types of Upset Bolts
Upset bolts are divided into two main categories including single and double upset bolts.
The main difference between the two types of upset bolts is in the number of forged plates.
 Types of upset bolts
Types of upset bolts
Single Upset Bolt has fewer forged plates on one side of the bolt.
Double Upset Bolts have more forged plates on both sides of the bolt.
Main Applications of Upset Bolts
You can use upset bolts on the side of the pole installation to support secondary service wires and neutral conductors.
Double upset bolt provides an allowance of between 1 – 5/8 inches between the pole and the insulator.
The main function is to provide support to the insulator pin for power wires and conductors passing through.
Parts of Upset Bolts
Upset bolt can be an assembly of different parts and components.
In this section, I am going to take you through this:
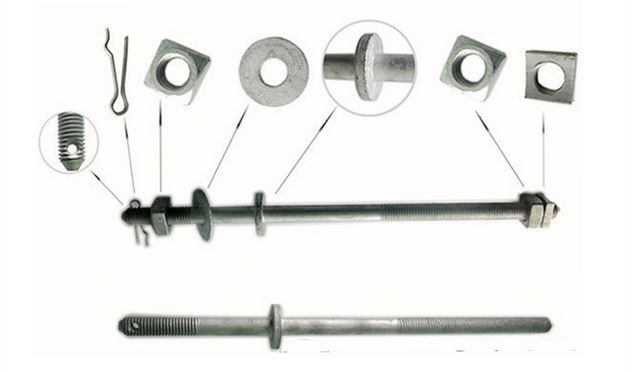
Parts of upset bolt
a) Forged Plate
The forged plate protects the insulator pin from falling off the upset bolt.
b) Insulator Pin
It is one of the most important parts of the upset bolt.
It goes across a particular end of the upset bolt.
Insulator pin insulates the secondary service wires and the conductor.
c) Round washer
It is a type of flat washer that is circular in shape and has a hole at the center.
The hole at the center is slightly wider than the diameter of the upset bolt.
It distributes the load of the upset bolt and buts evenly improving its durability.
d) Square nuts
It is a nut with four sides increasing the surface with the areas that are being fastened.
It provides resistance to the loosening of the fastened material held in place with the upset bolt.
It is not likely to be rounded after a series of tightening and loosening cycles.
e) Lock nuts
Lock nuts or prevailing torque nuts are a type of nut that will resist loosening of the upset bolt after vibration.
It has a particular portion that deforms especially as you fasten the nut making it lock.
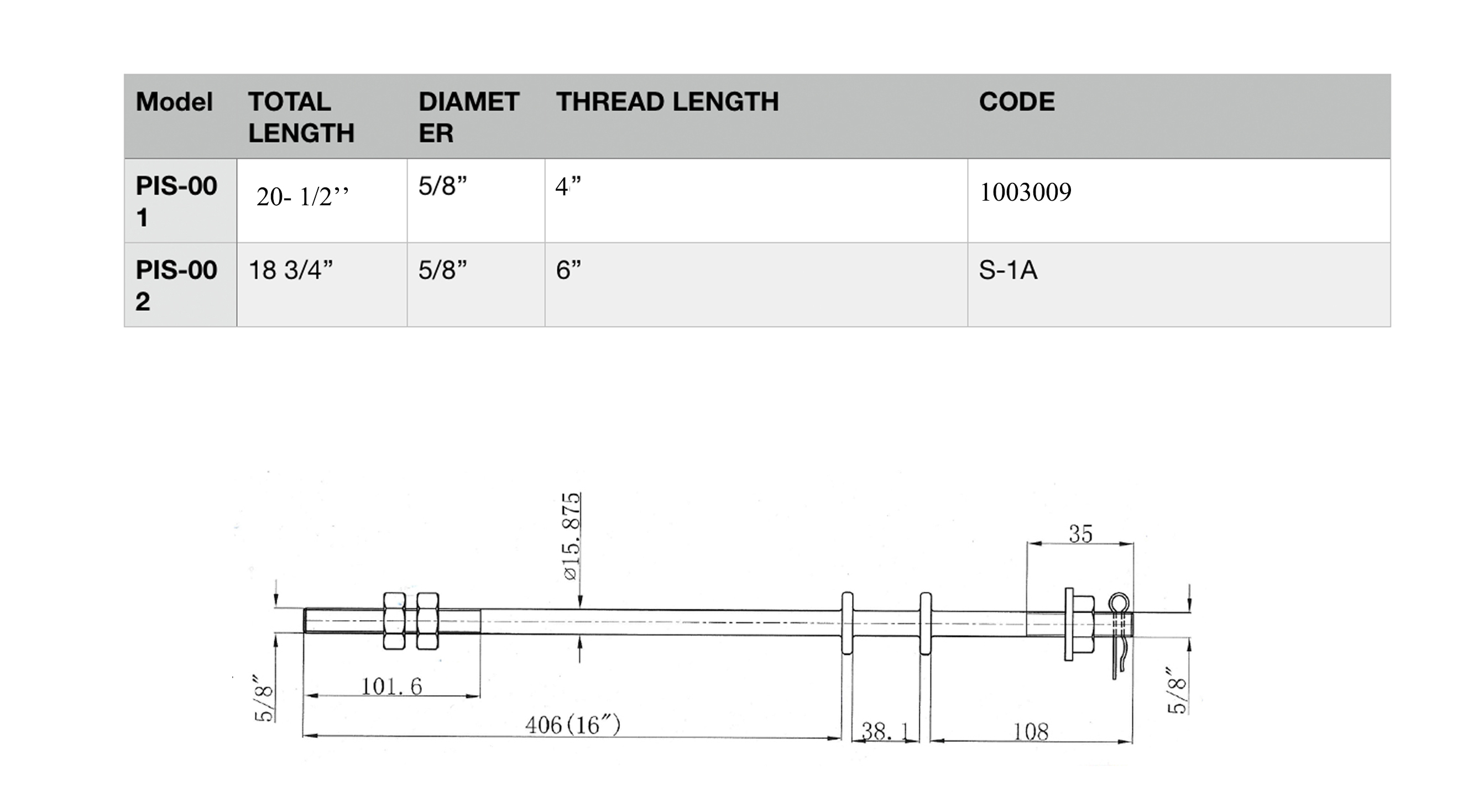
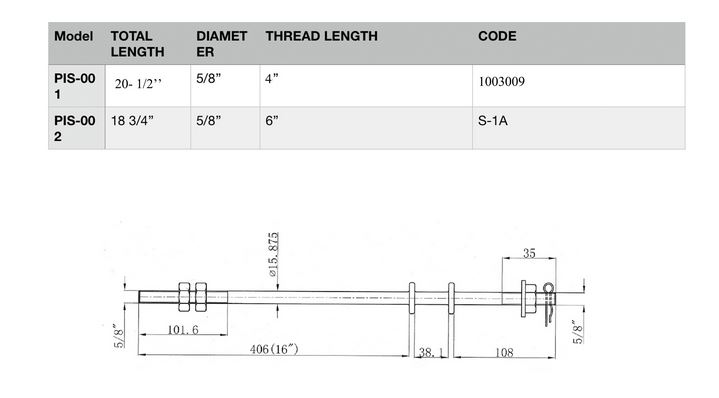
Technical Specifications of Upset Bolts
Some of the main technical specifications of upset bolts include:
Technical specification of upset bolt
Technical specification of Upset bolt
· Diameter
When you are looking for an upset bolt of a particular size, you will come across dimensions such as diameter.
Apart from that, you will also come across the length of the stem or the length of the shank.
These are the main dimensions that you should know when looking for or making an order for an upset bolt.
As an example, you can identify a bolt as “½ inch by 6 inches” or “1/2-inch bolt 6 inches long”.
This means that the bolt you are referring to has a shank that is ½ an inch in diameter.
It also has a length of 6 inches from the stem end to the side right under the head.
Bolt head dimensions are similar for bolts of the same size which you can determine by measuring the diameter of the shank.
It is the distance running across the head of the bolt from one flat end to another flat end.
The thickness of the head is also similar in all bolts of the same size.
· Material Type
Forging a spool bolt or an upset bolt requires iron or carbon steel as the main raw material.
The material can either have a double or a single integral washer which is upset at the end of the insulator.
The type of material you will use will determine the type of process you will use in manufacturing the upset bolt.
Apart from that, the material determines the tensile strength of the upset bolt.
This means that, the stronger the material, the greater the tensile strength.
Most of the elements are susceptible to corrosion and have to go through the process of hot-dip galvanization.
· Finish – Hot Dip Galvanization
The process of hot-dip galvanization involves dipping the upset bolt into molten zinc.
The reaction of the material and molten zinc will form a coat around the bolt.
The coat makes it more resistant to corrosion thus a longer life and more strength.
Apart from that, hot-dip galvanization gives it a smooth and polished finish.
It makes it more attractive and appealing to the eye.
· Tensile strength
The tensile strength of the upset bolt depends on different factors in the material and manufacturing process.
Stronger materials are better as they improve the tensile strength of the upset bolt.
Handmade upset bolts have lower tensile strength as compared to those from machines.
The reason behind it lies in the fact that some of the upset bolts you will make by hand will require welding.
At some point, it might break at the point where welding was done making it weaker.
· Standard Specifications
Manufacturing and hot-dip galvanization of upset bolts follow the ASTM A-153 standard of specification.
It applies to iron and steel hardware that passes through the process of hot-dip galvanization to provide a zinc coat.
It applies to steel hardware of class A, B, C and D as the thickness vary depending on the material in use.
The upset bolt will conform to ANSI C135.31 and supports a load of 800 pounds and an angle of deflection of 10 degrees.
This mode of standardization is in use in the United States proving that standardization varies in different countries.
Manufacturing Process of Upset Bolts
There are two main processes you will come across when it comes to the manufacture of upset bolts.
Upset bolts manufacturing processes include welding the heads and upsetting in small bolts and bolts from machines.
This means that the upsetting process is standard on small bolts and bolts made from machines.
Welding an upset bolt is very easy but it is not the best method of making the upset bolt.
The upset bolt you will make from this process is weak as compared to the others.
It can easily break under a lot of pressure.
It is also possible to manufacture large quantities of bolts at the same time using machines.
The first step is collecting all the relevant raw materials required for the process.
The metal bars are heated at very high temperatures in a furnace.
You have to be very careful when handling metal heated at very high temperatures and put on protective clothing.
After that, you will pass the heated metal bars through a machine that will make the heads of the bolts.
The machines are usually automated and you will determine the right dimensions of the bolt before passing it through the machine.
The machines will make the heads according to the aspects that you will direct it to make.
Technical drawing of upset bolt
After that, you will pass the bolt through the process of hot-dip galvanization to make it resistant to corrosion.
You will dip the bolts in molten zinc and leave them for a while for the reaction to occur.
It will form a coat on the bolt that will make it resistant to corrosion and give it a fine shiny finish.
In most cases, when doing the work by hand, the machines in use are usually of elementary characters.
The device you will use in making the head of the upset bolt is known as a header.
The header consists of a disc which has a hole drilled in accordance to the thickness of the upset bolt.
It also has a handle with a length usually 12 or 15 inches.
The hole should be 1/32 inches wider than the standard size of the iron you will use in making the bolt.
Making a bolt using this machine requires you to cut the iron to the length that you need.
After that, heat the side of the bolt where you will make the head of the upset bolt.
Observe the iron as it heats to a dull straw color and then strike it against an anvil.
As you hit it against the anvil, upset it so that the head is not allowed to pass the header.
After that, place the hot end on the square part of the header to shape it appropriately.
The cold part of the iron will drop into the header then strike it till if forms the head.
Remove it and shape it properly on the anvil taking note of the edges and the face of the bolt.
You will need the help of an assistant to help you in the whole process of making the upset bolt.
The last step in all the processes mentioned above is the making of the threads on the upset bolts.
For the single upset bolts, you will make the treads on one side particularly away from the head.
For the double upset bolts, you will make the threads on both ends of the upset bolt.
Finally fit the nuts, insulator pins and washers accordingly.
Installation of Upset Bolts
Installing an upset bolt is a straightforward process that does not require the help of an expert.
In most cases, experts are hired to do the installation, but you can easily do it on your own.
You will assemble all the material you will require for the process of installation and have a ladder too.
Upset bolt
With the help of an assistant, assemble all the other connections and put them together.
In most cases, you will do the assembly on the ladder above the ground and the installation too.
Drill holes on the side of the post where you will insert the bolt.
The size of the hole should correspond to the size of the upset bolt you intend to use.
The upset bolt should also be long enough to pass through the pole and appear on the other side of the pole.
This is important especially if you will be fastening the nuts to the upset bolt.
After drilling the holes, position the other appliances well so that the holes match.
This means that the holes should be in a straight line to allow the upset bolt through.
Insert the upset bolt through the holes making sure that it appears on the other side.
Take the washers and the nuts and fit them well onto the upset bolt.
Using a spanner or pliers, fasten the nuts on both sides until it is strong enough.
Repeat the same process on the other upset bolts until the installation process is complete.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the function of an upset bolt?
The upset bolt is used with spool insulators to assemble on one side-pole to support the neutral conductors or power wire.
What are the types of upset bolts?
There are single upset bolt and double upset bolt.
What is the main progress to make the upset bolts?
The main process in making upset bolts is drop forged.
What is the standard of the upset bolt in your factory?
The upset bolt is made according to UNC.
How to choosing the manufacturer of upset bolts?
Here are the guidelines that can help you choose a suitable manufacturer:
- Check whether the company is licensed
- The production capacity of the company
- Look for the reviews about the manufacturer
- Experience of the manufacturer
Conclusion
You are now with the necessary information that will help you in making the right decision for a bolt.
Before you make an order, please have a look at the type of installation you would like to do.
After that, you are at liberty to call and order an upset bolt according to your specifications.
Here at Rax Industry we design and manufacture quality upset bolts.
Talk to us today for cost-competitive upset bolts.